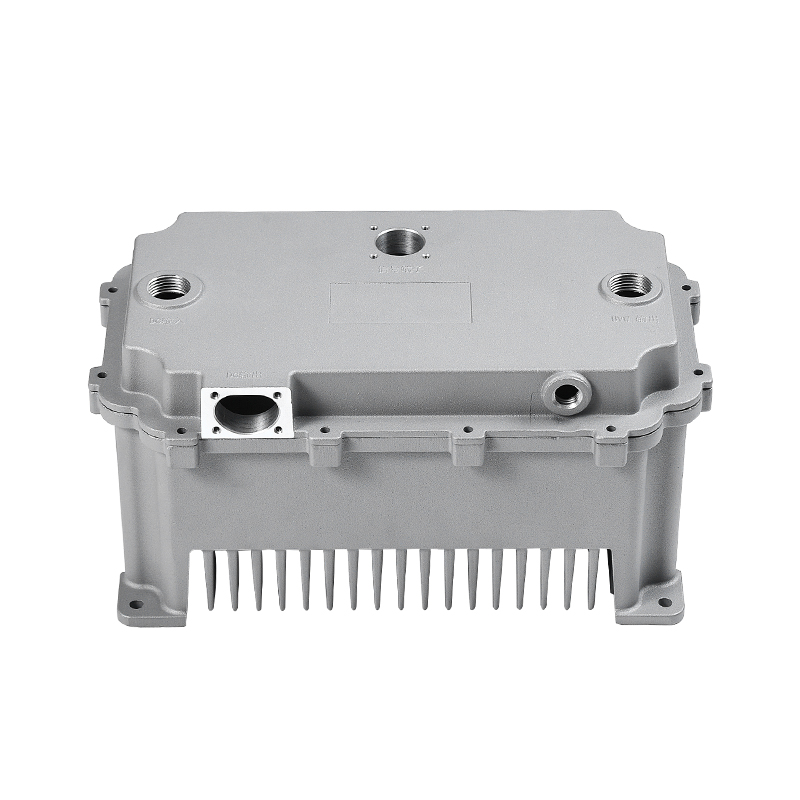
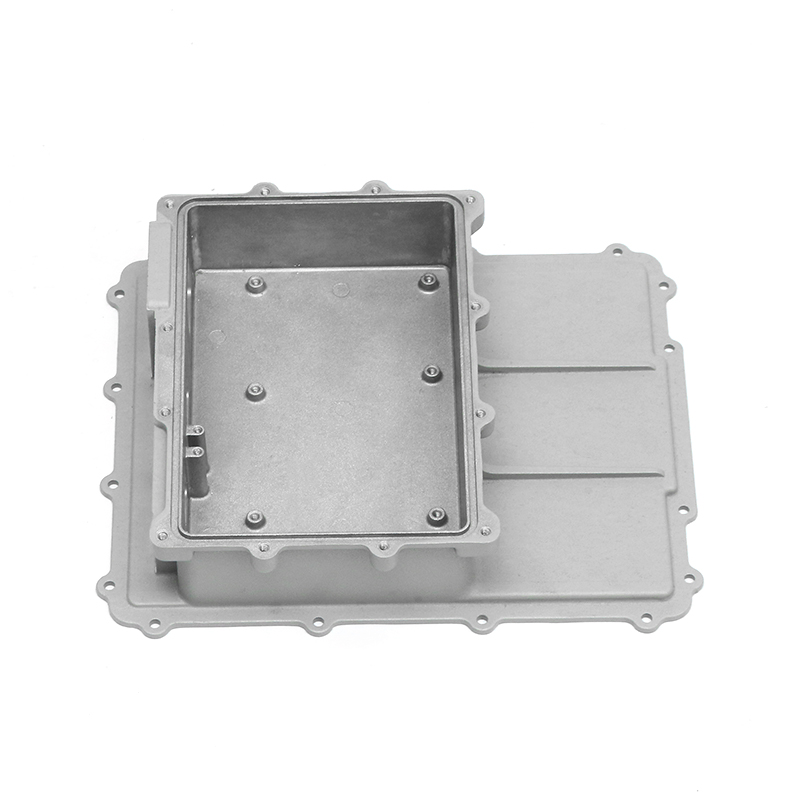
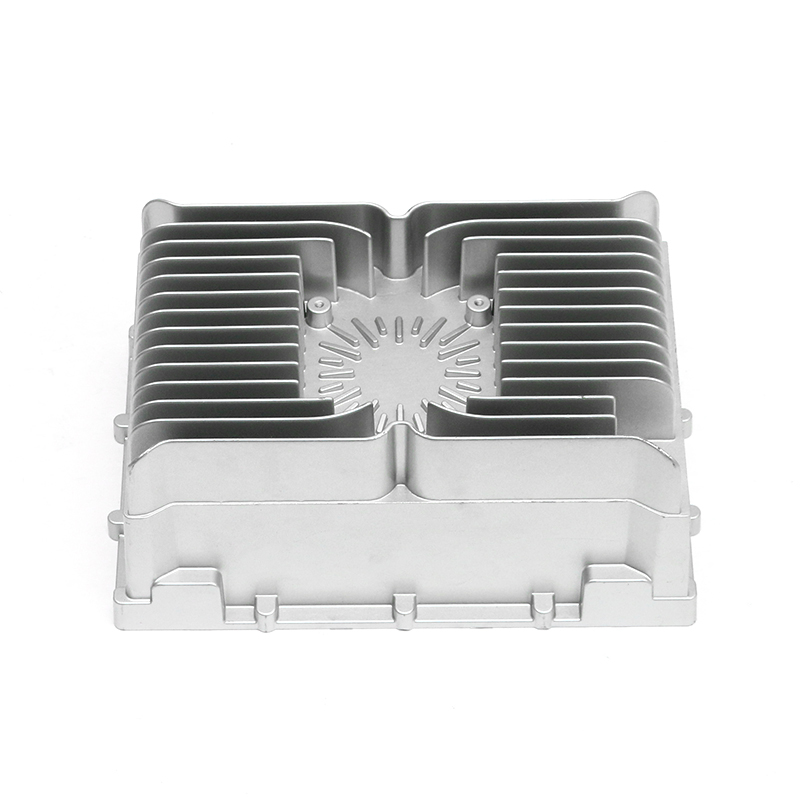
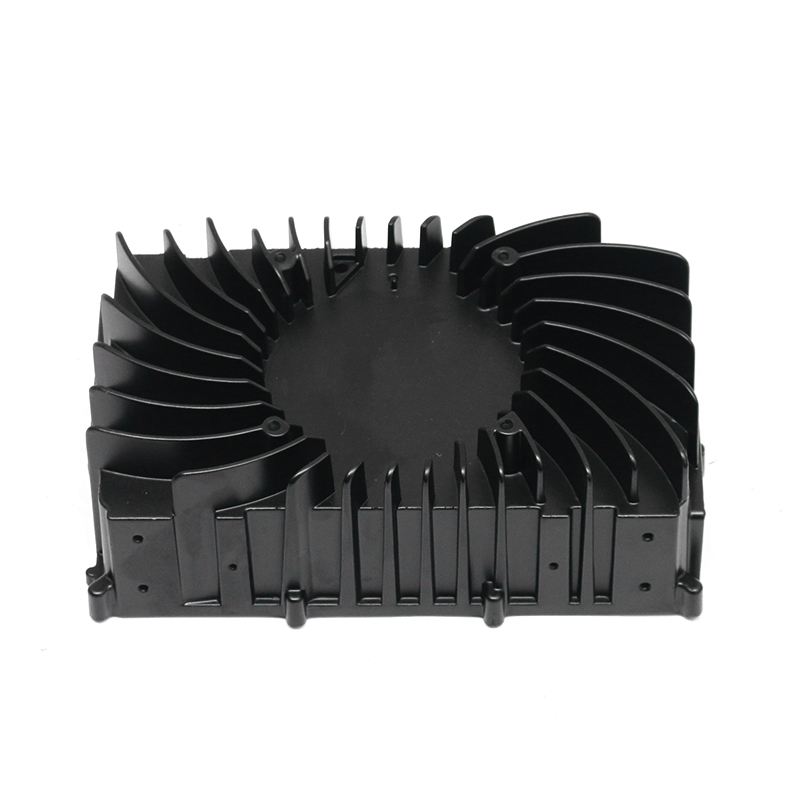
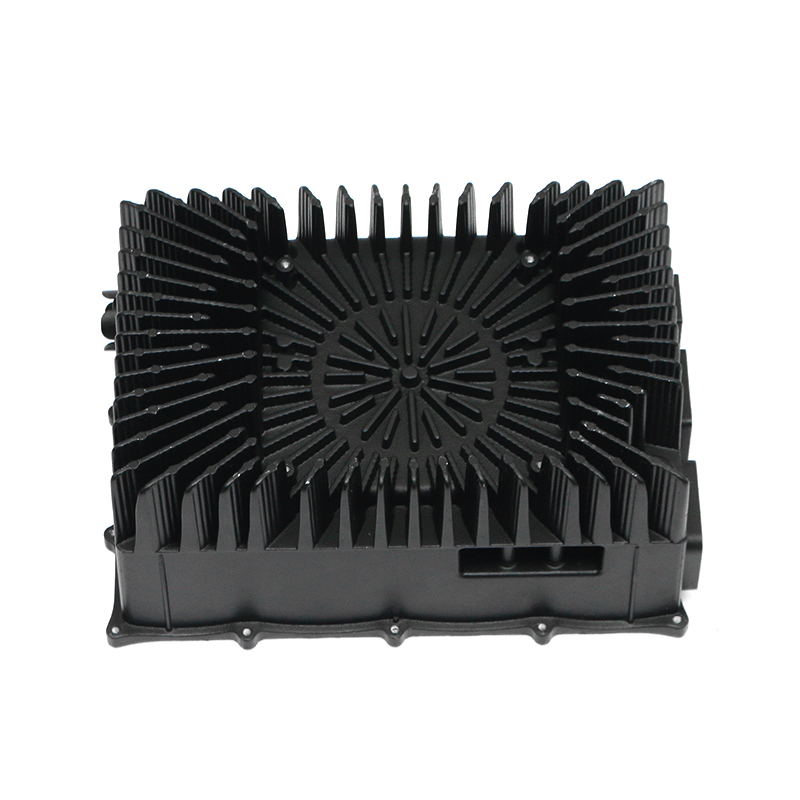
Den bil vandpumpe spiller en afgørende rolle i at opretholde en effektiv kølevæskecirkulation i hele motoren ved kontinuerligt at cirkulere kølervæske (normalt en blanding af vand og frostvæske) gennem motorblokken, køleren og kølesystemet. Dette hjælper med at holde motoren på en optimal driftstemperatur ved at overføre varme væk fra motoren og forhindre den i at overophedes.
Den car water pump is typically driven by the engine's crankshaft via a belt, chain, or sometimes by an electric motor (in the case of electric water pumps). As the pump rotates, it uses an impeller to move coolant through the engine.The impeller consists of several blades or vanes that direct the coolant towards the engine block and radiator. As the impeller spins, it creates a pressure differential that draws coolant into the pump and forces it into the engine's cooling passages.
Den car water pump sucks coolant from the bottom of the radiator (or coolant reservoir) through a suction inlet. The coolant is then passed through the pump's impeller, which increases the coolant's velocity and pressure as it is pushed out.
Den coolant is directed to flow through the engine block and cylinder head, where it absorbs the heat generated by the combustion process. It then returns to the radiator, where the heat is released into the surrounding air, and the coolant is cooled before being recirculated by the water pump.
Den thermostat plays a crucial role in regulating the temperature of the coolant and ensuring that it circulates at the optimal temperature range for engine efficiency. When the engine is cold, the thermostat remains closed to prevent coolant flow to the radiator, allowing the engine to warm up faster.
Når motoren når sin driftstemperatur, åbner termostaten, så kølevæsken kan strømme frit til køleren. Dette sikrer, at vandpumpen kun cirkulerer kølevæske, når motoren når den korrekte temperatur for effektiv køling.
Den car water pump ensures the coolant is circulated at the correct pressure and flow rate to achieve efficient heat dissipation. If the flow rate is too low, the coolant won't absorb enough heat from the engine, which can lead to overheating. Conversely, if the flow rate is too high, it could result in unnecessary energy consumption and reduced overall system efficiency.
Den pump is designed to match the engine's cooling demands by adjusting the flow based on factors such as engine speed, coolant temperature, and load conditions. Some modern vehicles use electronic control systems to regulate the speed of electric water pumps, adapting the flow to real-time conditions.
Den car water pump must be able to maintain an effective coolant circulation rate under varying engine conditions. As engine speed increases (e.g., during acceleration), the water pump speeds up to increase coolant flow, ensuring that the engine remains adequately cooled under high-performance conditions.
På den anden side, når motoren går i tomgang eller kører ved lave hastigheder, kan pumpen bremse ned, hvilket reducerer kølevæskestrømmen for at spare energi.
De fleste kølesystemer har et bypass-kredsløb, der tillader noget kølevæske at strømme direkte fra bilens vandpumpe til motoren uden at passere gennem køleren. Dette hjælper motoren med at nå driftstemperatur hurtigere, især ved koldstart, ved at sikre, at kølevæsken cirkulerer og varmes op, selv når termostaten er lukket.
Når termostaten åbner, strømmer kølevæsken gennem køleren, hvor den afkøles, inden den vender tilbage til motoren. Dette hjælper med at forhindre, at motoren overophedes i tomgang eller ved lav hastighed.
I moderne køretøjer, især hybrid- og elektriske køretøjer, er nogle bilers vandpumper designet til at variere kølevæskestrømmen baseret på motorens og kølesystemets realtidsbehov. For eksempel kan en elektrisk vandpumpe reguleres af køretøjets ECU (Electronic Control Unit) for at justere flowhastigheden i henhold til temperatur, motorbelastning og hastighed.
Anbefalede produkter
Produkter fra kendte virksomheder nyder stor tillid fra brugerne.